matutils – Math utils¶
Math helper functions.
- class gensim.matutils.Dense2Corpus(dense, documents_columns=True)¶
Bases:
objectTreat dense numpy array as a streamed Gensim corpus in the bag-of-words format.
Notes
No data copy is made (changes to the underlying matrix imply changes in the streamed corpus).
See also
corpus2dense()Convert Gensim corpus to dense matrix.
Sparse2CorpusConvert sparse matrix to Gensim corpus format.
- Parameters
dense (numpy.ndarray) – Corpus in dense format.
documents_columns (bool, optional) – Documents in dense represented as columns, as opposed to rows?
- class gensim.matutils.MmWriter(fname)¶
Bases:
objectStore a corpus in Matrix Market format, using
MmCorpus.Notes
The output is written one document at a time, not the whole matrix at once (unlike e.g. scipy.io.mmread). This allows you to write corpora which are larger than the available RAM.
The output file is created in a single pass through the input corpus, so that the input can be a once-only stream (generator).
To achieve this, a fake MM header is written first, corpus statistics are collected during the pass (shape of the matrix, number of non-zeroes), followed by a seek back to the beginning of the file, rewriting the fake header with the final values.
- Parameters
fname (str) – Path to output file.
- HEADER_LINE = b'%%MatrixMarket matrix coordinate real general\n'¶
- close()¶
Close self.fout file.
- fake_headers(num_docs, num_terms, num_nnz)¶
Write “fake” headers to file, to be rewritten once we’ve scanned the entire corpus.
- Parameters
num_docs (int) – Number of documents in corpus.
num_terms (int) – Number of term in corpus.
num_nnz (int) – Number of non-zero elements in corpus.
- static write_corpus(fname, corpus, progress_cnt=1000, index=False, num_terms=None, metadata=False)¶
Save the corpus to disk in Matrix Market format.
- Parameters
fname (str) – Filename of the resulting file.
corpus (iterable of list of (int, number)) – Corpus in streamed bag-of-words format.
progress_cnt (int, optional) – Print progress for every progress_cnt number of documents.
index (bool, optional) – Return offsets?
num_terms (int, optional) – Number of terms in the corpus. If provided, the corpus.num_terms attribute (if any) will be ignored.
metadata (bool, optional) – Generate a metadata file?
- Returns
offsets – List of offsets (if index=True) or nothing.
- Return type
{list of int, None}
Notes
Documents are processed one at a time, so the whole corpus is allowed to be larger than the available RAM.
See also
gensim.corpora.mmcorpus.MmCorpus.save_corpus()Save corpus to disk.
- write_headers(num_docs, num_terms, num_nnz)¶
Write headers to file.
- Parameters
num_docs (int) – Number of documents in corpus.
num_terms (int) – Number of term in corpus.
num_nnz (int) – Number of non-zero elements in corpus.
- write_vector(docno, vector)¶
Write a single sparse vector to the file.
- Parameters
docno (int) – Number of document.
vector (list of (int, number)) – Document in BoW format.
- Returns
Max word index in vector and len of vector. If vector is empty, return (-1, 0).
- Return type
(int, int)
- class gensim.matutils.Scipy2Corpus(vecs)¶
Bases:
objectConvert a sequence of dense/sparse vectors into a streamed Gensim corpus object.
See also
corpus2csc()Convert corpus in Gensim format to scipy.sparse.csc matrix.
- Parameters
vecs (iterable of {numpy.ndarray, scipy.sparse}) – Input vectors.
- class gensim.matutils.Sparse2Corpus(sparse, documents_columns=True)¶
Bases:
objectConvert a matrix in scipy.sparse format into a streaming Gensim corpus.
See also
corpus2csc()Convert gensim corpus format to scipy.sparse.csc matrix
Dense2CorpusConvert dense matrix to gensim corpus.
- Parameters
sparse (scipy.sparse) – Corpus scipy sparse format
documents_columns (bool, optional) – Documents will be column?
- gensim.matutils.any2sparse(vec, eps=1e-09)¶
Convert a numpy.ndarray or scipy.sparse vector into the Gensim bag-of-words format.
- Parameters
vec ({numpy.ndarray, scipy.sparse}) – Input vector
eps (float, optional) – Value used for threshold, all coordinates less than eps will not be presented in result.
- Returns
Vector in BoW format.
- Return type
list of (int, float)
- gensim.matutils.argsort(x, topn=None, reverse=False)¶
Efficiently calculate indices of the topn smallest elements in array x.
- Parameters
x (array_like) – Array to get the smallest element indices from.
topn (int, optional) – Number of indices of the smallest (greatest) elements to be returned. If not given, indices of all elements will be returned in ascending (descending) order.
reverse (bool, optional) – Return the topn greatest elements in descending order, instead of smallest elements in ascending order?
- Returns
Array of topn indices that sort the array in the requested order.
- Return type
numpy.ndarray
- gensim.matutils.blas(name, ndarray)¶
Helper for getting the appropriate BLAS function, using
scipy.linalg.get_blas_funcs().- Parameters
name (str) – Name(s) of BLAS functions, without the type prefix.
ndarray (numpy.ndarray) – Arrays can be given to determine optimal prefix of BLAS routines.
- Returns
BLAS function for the needed operation on the given data type.
- Return type
object
- gensim.matutils.corpus2csc(corpus, num_terms=None, dtype=<class 'numpy.float64'>, num_docs=None, num_nnz=None, printprogress=0)¶
Convert a streamed corpus in bag-of-words format into a sparse matrix scipy.sparse.csc_matrix, with documents as columns.
Notes
If the number of terms, documents and non-zero elements is known, you can pass them here as parameters and a (much) more memory efficient code path will be taken.
- Parameters
corpus (iterable of iterable of (int, number)) – Input corpus in BoW format
num_terms (int, optional) – Number of terms in corpus. If provided, the corpus.num_terms attribute (if any) will be ignored.
dtype (data-type, optional) – Data type of output CSC matrix.
num_docs (int, optional) – Number of documents in corpus. If provided, the corpus.num_docs attribute (in any) will be ignored.
num_nnz (int, optional) – Number of non-zero elements in corpus. If provided, the corpus.num_nnz attribute (if any) will be ignored.
printprogress (int, optional) – Log a progress message at INFO level once every printprogress documents. 0 to turn off progress logging.
- Returns
corpus converted into a sparse CSC matrix.
- Return type
scipy.sparse.csc_matrix
See also
Sparse2CorpusConvert sparse format to Gensim corpus format.
- gensim.matutils.corpus2dense(corpus, num_terms, num_docs=None, dtype=<class 'numpy.float32'>)¶
Convert corpus into a dense numpy 2D array, with documents as columns.
- Parameters
corpus (iterable of iterable of (int, number)) – Input corpus in the Gensim bag-of-words format.
num_terms (int) – Number of terms in the dictionary. X-axis of the resulting matrix.
num_docs (int, optional) – Number of documents in the corpus. If provided, a slightly more memory-efficient code path is taken. Y-axis of the resulting matrix.
dtype (data-type, optional) – Data type of the output matrix.
- Returns
Dense 2D array that presents corpus.
- Return type
numpy.ndarray
See also
Dense2CorpusConvert dense matrix to Gensim corpus format.
- gensim.matutils.cossim(vec1, vec2)¶
Get cosine similarity between two sparse vectors.
Cosine similarity is a number between <-1.0, 1.0>, higher means more similar.
- Parameters
vec1 (list of (int, float)) – Vector in BoW format.
vec2 (list of (int, float)) – Vector in BoW format.
- Returns
Cosine similarity between vec1 and vec2.
- Return type
float
- gensim.matutils.dense2vec(vec, eps=1e-09)¶
Convert a dense numpy array into the Gensim bag-of-words format.
- Parameters
vec (numpy.ndarray) – Dense input vector.
eps (float) – Feature weight threshold value. Features with abs(weight) < eps are considered sparse and won’t be included in the BOW result.
- Returns
BoW format of vec, with near-zero values omitted (sparse vector).
- Return type
list of (int, float)
See also
sparse2full()Convert a document in Gensim bag-of-words format into a dense numpy array.
- gensim.matutils.full2sparse(vec, eps=1e-09)¶
Convert a dense numpy array into the Gensim bag-of-words format.
- Parameters
vec (numpy.ndarray) – Dense input vector.
eps (float) – Feature weight threshold value. Features with abs(weight) < eps are considered sparse and won’t be included in the BOW result.
- Returns
BoW format of vec, with near-zero values omitted (sparse vector).
- Return type
list of (int, float)
See also
sparse2full()Convert a document in Gensim bag-of-words format into a dense numpy array.
- gensim.matutils.full2sparse_clipped(vec, topn, eps=1e-09)¶
Like
full2sparse(), but only return the topn elements of the greatest magnitude (abs).This is more efficient that sorting a vector and then taking the greatest values, especially where len(vec) >> topn.
- Parameters
vec (numpy.ndarray) – Input dense vector
topn (int) – Number of greatest (abs) elements that will be presented in result.
eps (float) – Threshold value, if coordinate in vec < eps, this will not be presented in result.
- Returns
Clipped vector in BoW format.
- Return type
list of (int, float)
See also
full2sparse()Convert dense array to gensim bag-of-words format.
- gensim.matutils.hellinger(vec1, vec2)¶
Calculate Hellinger distance between two probability distributions.
- Parameters
vec1 ({scipy.sparse, numpy.ndarray, list of (int, float)}) – Distribution vector.
vec2 ({scipy.sparse, numpy.ndarray, list of (int, float)}) – Distribution vector.
- Returns
Hellinger distance between vec1 and vec2. Value in range [0, 1], where 0 is min distance (max similarity) and 1 is max distance (min similarity).
- Return type
float
- gensim.matutils.isbow(vec)¶
Checks if a vector is in the sparse Gensim bag-of-words format.
- Parameters
vec (object) – Object to check.
- Returns
Is vec in BoW format.
- Return type
bool
- gensim.matutils.ismatrix(m)¶
Check whether m is a 2D numpy.ndarray or scipy.sparse matrix.
- Parameters
m (object) – Object to check.
- Returns
Is m a 2D numpy.ndarray or scipy.sparse matrix.
- Return type
bool
- gensim.matutils.jaccard(vec1, vec2)¶
Calculate Jaccard distance between two vectors.
- Parameters
vec1 ({scipy.sparse, numpy.ndarray, list of (int, float)}) – Distribution vector.
vec2 ({scipy.sparse, numpy.ndarray, list of (int, float)}) – Distribution vector.
- Returns
Jaccard distance between vec1 and vec2. Value in range [0, 1], where 0 is min distance (max similarity) and 1 is max distance (min similarity).
- Return type
float
- gensim.matutils.jaccard_distance(set1, set2)¶
Calculate Jaccard distance between two sets.
- Parameters
set1 (set) – Input set.
set2 (set) – Input set.
- Returns
Jaccard distance between set1 and set2. Value in range [0, 1], where 0 is min distance (max similarity) and 1 is max distance (min similarity).
- Return type
float
- gensim.matutils.jensen_shannon(vec1, vec2, num_features=None)¶
Calculate Jensen-Shannon distance between two probability distributions using scipy.stats.entropy.
- Parameters
vec1 ({scipy.sparse, numpy.ndarray, list of (int, float)}) – Distribution vector.
vec2 ({scipy.sparse, numpy.ndarray, list of (int, float)}) – Distribution vector.
num_features (int, optional) – Number of features in the vectors.
- Returns
Jensen-Shannon distance between vec1 and vec2.
- Return type
float
Notes
This is a symmetric and finite “version” of
gensim.matutils.kullback_leibler().
- gensim.matutils.kullback_leibler(vec1, vec2, num_features=None)¶
Calculate Kullback-Leibler distance between two probability distributions using scipy.stats.entropy.
- Parameters
vec1 ({scipy.sparse, numpy.ndarray, list of (int, float)}) – Distribution vector.
vec2 ({scipy.sparse, numpy.ndarray, list of (int, float)}) – Distribution vector.
num_features (int, optional) – Number of features in the vectors.
- Returns
Kullback-Leibler distance between vec1 and vec2. Value in range [0, +∞) where values closer to 0 mean less distance (higher similarity).
- Return type
float
- gensim.matutils.pad(mat, padrow, padcol)¶
Add additional rows/columns to mat. The new rows/columns will be initialized with zeros.
- Parameters
mat (numpy.ndarray) – Input 2D matrix
padrow (int) – Number of additional rows
padcol (int) – Number of additional columns
- Returns
Matrix with needed padding.
- Return type
numpy.matrixlib.defmatrix.matrix
- gensim.matutils.qr_destroy(la)¶
Get QR decomposition of la[0].
- Parameters
la (list of numpy.ndarray) – Run QR decomposition on the first elements of la. Must not be empty.
- Returns
Matrices
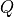 and
and 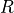 .
.- Return type
(numpy.ndarray, numpy.ndarray)
Notes
Using this function is less memory intense than calling scipy.linalg.qr(la[0]), because the memory used in la[0] is reclaimed earlier. This makes a difference when decomposing very large arrays, where every memory copy counts.
Warning
Content of la as well as la[0] gets destroyed in the process. Again, for memory-effiency reasons.
- gensim.matutils.ret_log_normalize_vec(vec, axis=1)¶
- gensim.matutils.ret_normalized_vec(vec, length)¶
Normalize a vector in L2 (Euclidean unit norm).
- Parameters
vec (list of (int, number)) – Input vector in BoW format.
length (float) – Length of vector
- Returns
L2-normalized vector in BoW format.
- Return type
list of (int, number)
- gensim.matutils.scipy2scipy_clipped(matrix, topn, eps=1e-09)¶
Get the ‘topn’ elements of the greatest magnitude (absolute value) from a scipy.sparse vector or matrix.
- Parameters
matrix (scipy.sparse) – Input vector or matrix (1D or 2D sparse array).
topn (int) – Number of greatest elements, in absolute value, to return.
eps (float) – Ignored.
- Returns
Clipped matrix.
- Return type
scipy.sparse.csr.csr_matrix
- gensim.matutils.scipy2sparse(vec, eps=1e-09)¶
Convert a scipy.sparse vector into the Gensim bag-of-words format.
- Parameters
vec (scipy.sparse) – Sparse vector.
eps (float, optional) – Value used for threshold, all coordinates less than eps will not be presented in result.
- Returns
Vector in Gensim bag-of-words format.
- Return type
list of (int, float)
- gensim.matutils.sparse2full(doc, length)¶
Convert a document in Gensim bag-of-words format into a dense numpy array.
- Parameters
doc (list of (int, number)) – Document in BoW format.
length (int) – Vector dimensionality. This cannot be inferred from the BoW, and you must supply it explicitly. This is typically the vocabulary size or number of topics, depending on how you created doc.
- Returns
Dense numpy vector for doc.
- Return type
numpy.ndarray
See also
full2sparse()Convert dense array to gensim bag-of-words format.
- gensim.matutils.unitvec(vec, norm='l2', return_norm=False)¶
Scale a vector to unit length.
- Parameters
vec ({numpy.ndarray, scipy.sparse, list of (int, float)}) – Input vector in any format
norm ({'l1', 'l2', 'unique'}, optional) – Metric to normalize in.
return_norm (bool, optional) – Return the length of vector vec, in addition to the normalized vector itself?
- Returns
numpy.ndarray, scipy.sparse, list of (int, float)} – Normalized vector in same format as vec.
float – Length of vec before normalization, if return_norm is set.
Notes
Zero-vector will be unchanged.
- gensim.matutils.veclen(vec)¶
Calculate L2 (euclidean) length of a vector.
- Parameters
vec (list of (int, number)) – Input vector in sparse bag-of-words format.
- Returns
Length of vec.
- Return type
float
- gensim.matutils.zeros_aligned(shape, dtype, order='C', align=128)¶
Get array aligned at align byte boundary in memory.
- Parameters
shape (int or (int, int)) – Shape of array.
dtype (data-type) – Data type of array.
order ({'C', 'F'}, optional) – Whether to store multidimensional data in C- or Fortran-contiguous (row- or column-wise) order in memory.
align (int, optional) – Boundary for alignment in bytes.
- Returns
Aligned array.
- Return type
numpy.ndarray
